1.前言
虽然工作中优先队列,甚至队列用的都不多,也不怎么熟悉他们的原理和使用,这几天求知欲突发,很好奇一个优先队列到底怎么实现的,且感觉以后会用上,于是看了一下PriorityQueue源码(jdk1.8),记录一下学习过程,还是有许多收获。PriorityQueue 也是Java集合框架的成员,继承AbstractQueue,AbstractQueue继承了AbstractCollection并实现了queue接口。
2.原理
PriorityQueue 基于平衡二叉堆的无界队列,不允许空元素,当容量不足会自动扩容,虽然是无界的但是最大的容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE ;通过平衡二叉堆实现,具体说是通过完全二叉树(complete binary tree)实现的小顶堆(任意一个非叶子节点的权值,都不大于其左右子节点的权值),其底层实现是一个Object数组,队列的元素按照自然顺序或者指定的比较器排序,API文档描述
Priority queue represented as a balanced binary heap: the two children of queue[n] are queue[2n+1] and queue[2(n+1)]. The priority queue is ordered by comparator, or by the elements’natural ordering, if comparator is null: For each node n in the heap and each descendant d of n, n <= d. The element with the lowest value is in queue[0], assuming the queue is non empty.
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
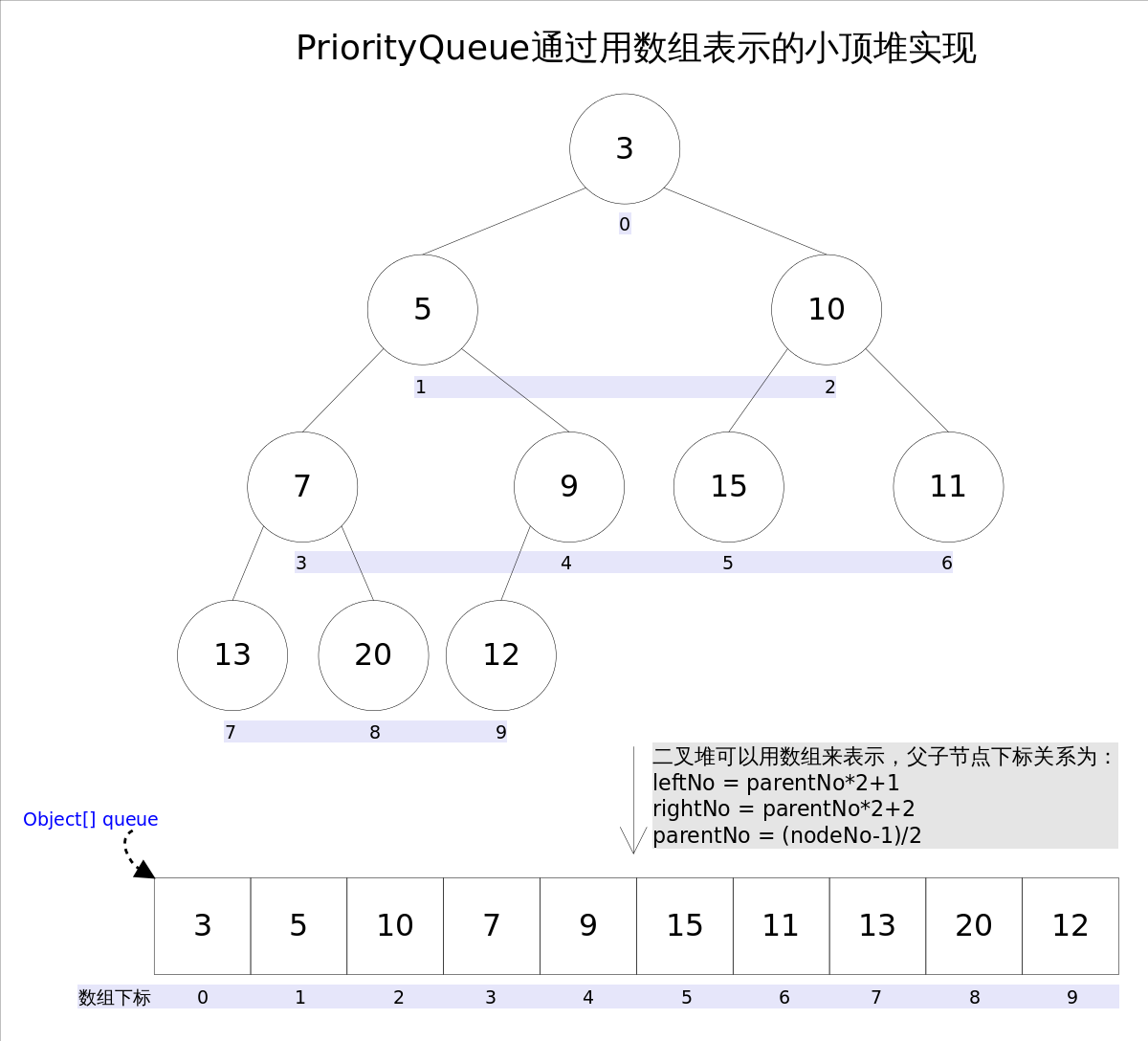
优先队列神奇的地方在于,无论你对队列做添加,删除元素等操作,它总能保证队列头部元素是权重最小的,想知道它是怎么实现的就跟着我来一起看看源码吧。
3.源码分析
主要分析一些比较复杂的方法,这些方法涉及到队列元素变动时对二叉堆顶元素权重最小的保持。
3.1 添加元素
PriorityQueue有两个添加元素方法,add(E)和offer(E),add方法是Collection接口里的,offer是Queue接口的方法,add调用offer方法,所以两个方法么有区别。我们看下offer方法的源码
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
//默认插入为止为队列尾部
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
//扩容
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e; //队列为空 就插入队列头部
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
当size大于等于queue数组的长度就是扩容的时候了,其中hugeCapacity方法就是把queue最大长度变成 Integer.MAX_VALUE
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}添加元素的主要逻辑还是在 siftUp(int, E)
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
* its parent, or is the root.
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}刚开始看这段代码时不了解完全二叉树的概念,虽然能看懂代码但要理解为何要这么操作就很吃力了,直到看到博客上讲关于PriorityQueue的文章才解开疑惑,本文中图片引用于那篇博文。下面这个图就形象的说明这个操作的过程。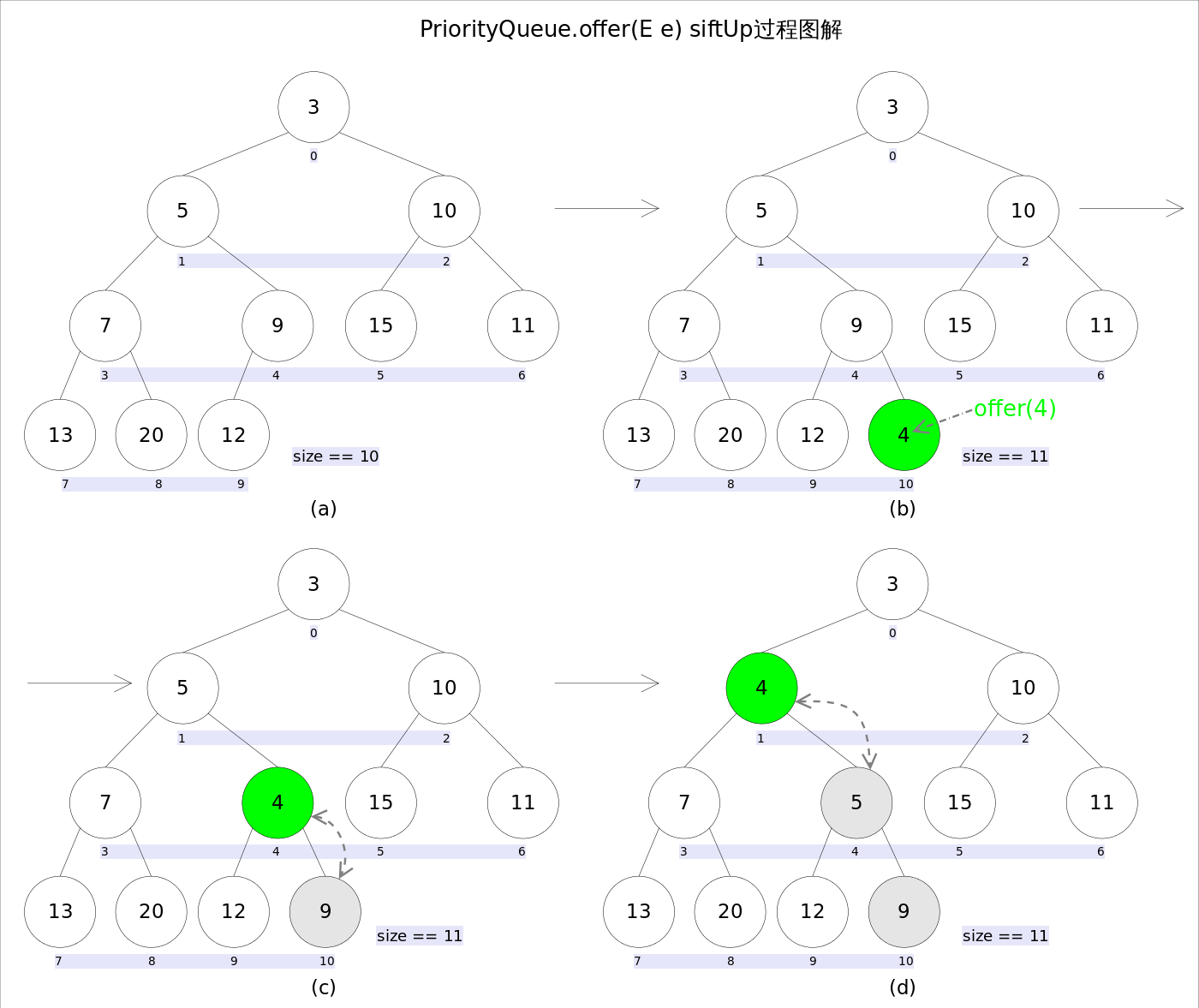
插入的元素处于k位置,先判断k节点元素与它的父节点元素的大小,如果大于父节点直接跳出循环,把插入的元素放入k位置,否则 交换k节点和它的父节点的元素值,并把k的值修改为父节点的位置,再拿新的k节点与它的父节点比较,还不满足条件就直到找到根节点为止。
3.2 弹出并删除队首元素
queue接口的poll方法能够返回队列的第一个元素并把它从队列里删除,这一节分析了往队列尾部添加元素如何保证队列的顺序,这次来看看它的反操作,把元素从队列头部删除如何保证优先队列的顺序。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or
* equal to its children or is a leaf.
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftDownComparable(k, x);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}删除队首元素并保证队首元素权重是最小值的逻辑在siftDown(int,E)里面,基本流程:
- 1 找到根节点的左子节点和右子节点,拿其中更小的元素与队尾元素比较;
- 2.1 如果子节点中较小的比队尾元素还大,则跳出循环;
- 2.2 如果队尾元素比子节点要大,则把子节点中较小值放入队列中的第k个位置,并把这个较小值所在位置赋值给k,继续查询k位置节点的左右子节点;
- 3 如此循环直到while条件不满足,最后把队尾元素插入k的位置。
要是没有图片辅助,光看代码还是有点难懂的,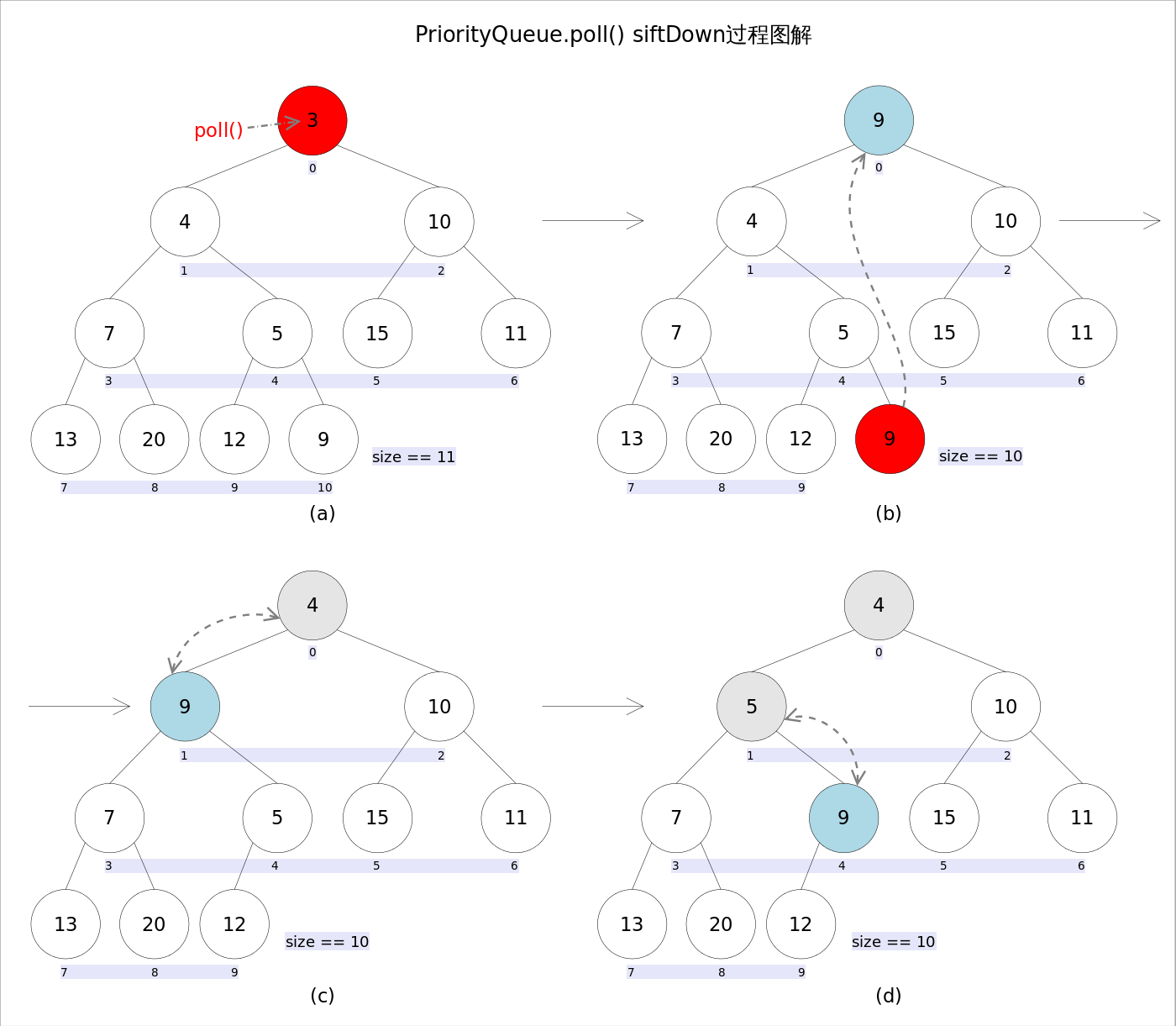
3.3 删除指定元素
remove(Object o)用来删除队列中与元素为o相等的元素,如果有多个删除其中一个,此方法有点类似poll方法,只是remove方法删除的元素可能是在任意位置,情况会稍微复杂些,需要从队列的第i个元素处调用一次siftDown。
/**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,
* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such
* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such
* elements. Returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contained
* the specified element (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a
* result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int i = indexOf(o);
if (i == -1)
return false;
else {
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
}
/**
* Removes the ith element from queue.
*
* Normally this method leaves the elements at up to i-1,
* inclusive, untouched. Under these circumstances, it returns
* null. Occasionally, in order to maintain the heap invariant,
* it must swap a later element of the list with one earlier than
* i. Under these circumstances, this method returns the element
* that was previously at the end of the list and is now at some
* position before i. This fact is used by iterator.remove so as to
* avoid missing traversing elements.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private E removeAt(int i) {
// assert i >= 0 && i < size;
modCount++;
int s = --size;
if (s == i) // removed last element
queue[i] = null;
else {
E moved = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
siftDown(i, moved);
if (queue[i] == moved) {
siftUp(i, moved);
if (queue[i] != moved)
return moved;
}
}
return null;
}********4.总结
如果要深入看懂PriorityQueue源码,需要有二叉堆的基础知识,否则就算能看懂每行代码,也不知道为何要这么写。另外优先队列是线程不安全的,多线程情况下不应该并发访问PriorityQueue,作为替代,可以访问线程安全的PriorityBlockingQueue。最后要说的是,往队列里添加删除元素 add,offer,remove(),poll这些实现的方法能保证O(log(n))的时间复杂度,remove(Object) ,contains(Object)操作提供的时间复杂度是O(n),因为最坏的情况会检索队列中的每个元素,检索方法 peek,element,size方法操作提供常数时间复杂度。
